เคสจัดฟันในวัย 35 กับการผ่าฟันฝัง มีผลกระทบหลังจัดฟันอย่างไร!
รีวิวเคสจัดฟัน ของคลินิกทันตกรรมเดอะคราวน์โคราช เป็นเคสที่มีการสบฟันแบบฟันหน้าล่างคร่อมฟันหน้าบน ระนาบสบฟันเอียงเมื่อมองจากทางด้านหน้า กระดูกขากรรไกรด้านขวาและฟันขวาของคนไข้ยุบ ส่งผลให้เมื่อคนไข้ยิ้มหรือพูดคุย จะดูใบหน้าไม่สมมาตร จากการประเมินสภาพช่องปาก และภายถ่ายรังสี มีโอกาสแก้ไขฟันได้ด้วยการจัดฟัน

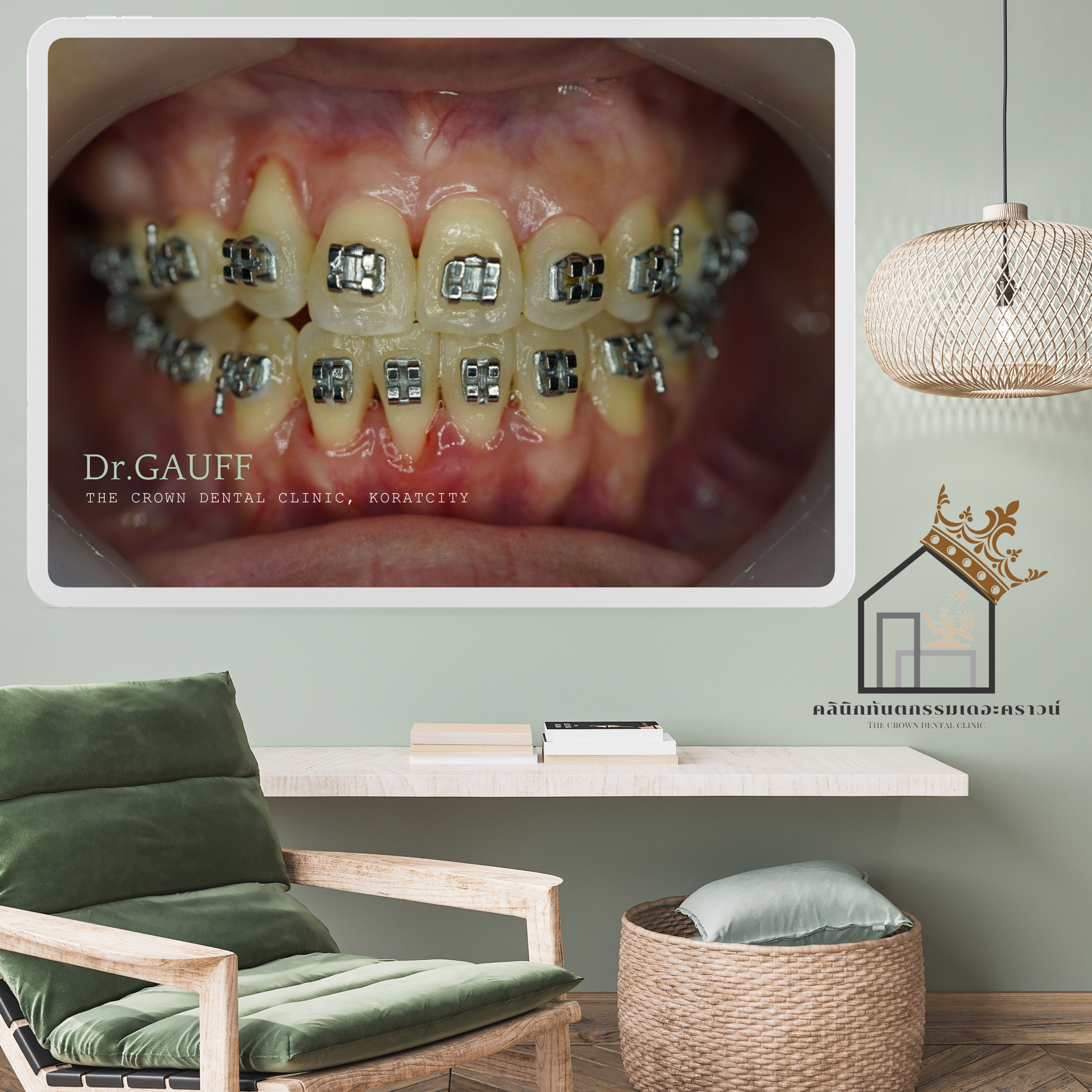
บริเวณด้านขวาของคนไข้ จากภาพจะเห็นการยุบตัวของฟันบริเวณนี้ และตรวจไม่พบฟันเขี้ยวขวาบน เมื่อเช็คภาพถ่ายรังสีเอ็กซ์เรย์ พบฟันเขี้ยวฝังในกระดูก พิจารณาผ่าตัดเพื่อนำฟันฝังออก ลงโอกาสเสี่ยงในการเกิดรอยโรคที่รุงแรง และฟันฝังยังมีผลต่อการเคลื่อนฟัน
แต่สิ่งที่ต้องคำนึงในการผ่าฟันฝังซี่นี้ออกคือ ในระหว่างการผ่าฟันฝัง จะมีการกรอกระดูกรอบฟันฝังออกด้วย แต่ฟันฝังมีตำแหน่งที่ใกล้ฟันซี่ที่ปกติค้างเคียง ส่งผลให้หลังการผ่าฟันฝัง คนไข้รายนี้จะพบโรคปริทันต์ของฟันข้างเคียงได้ เช่น ภาวะเหงือกร่น ร่องลึกปริทันต์ หรือแม้กระทั่งฟันโยก ได้
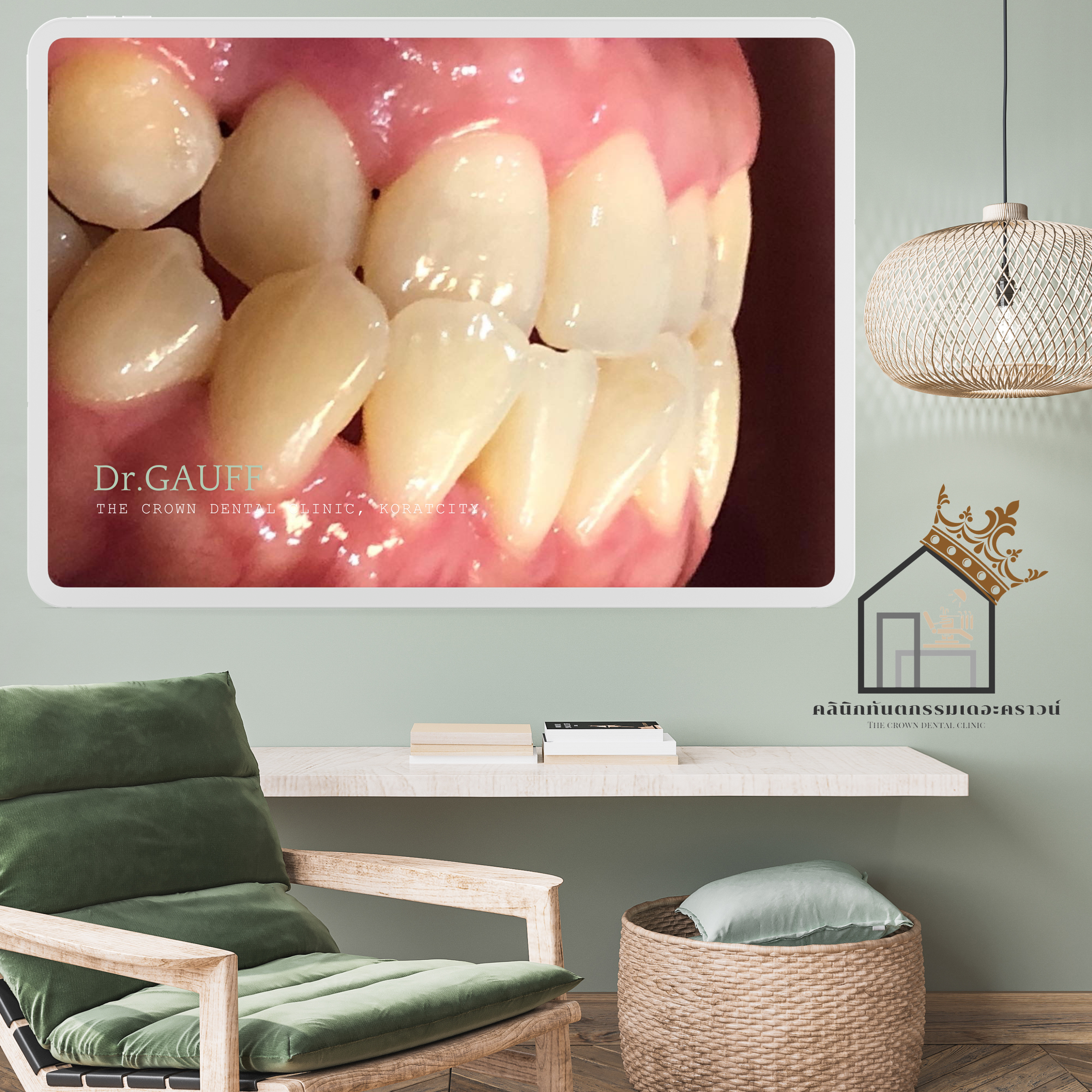
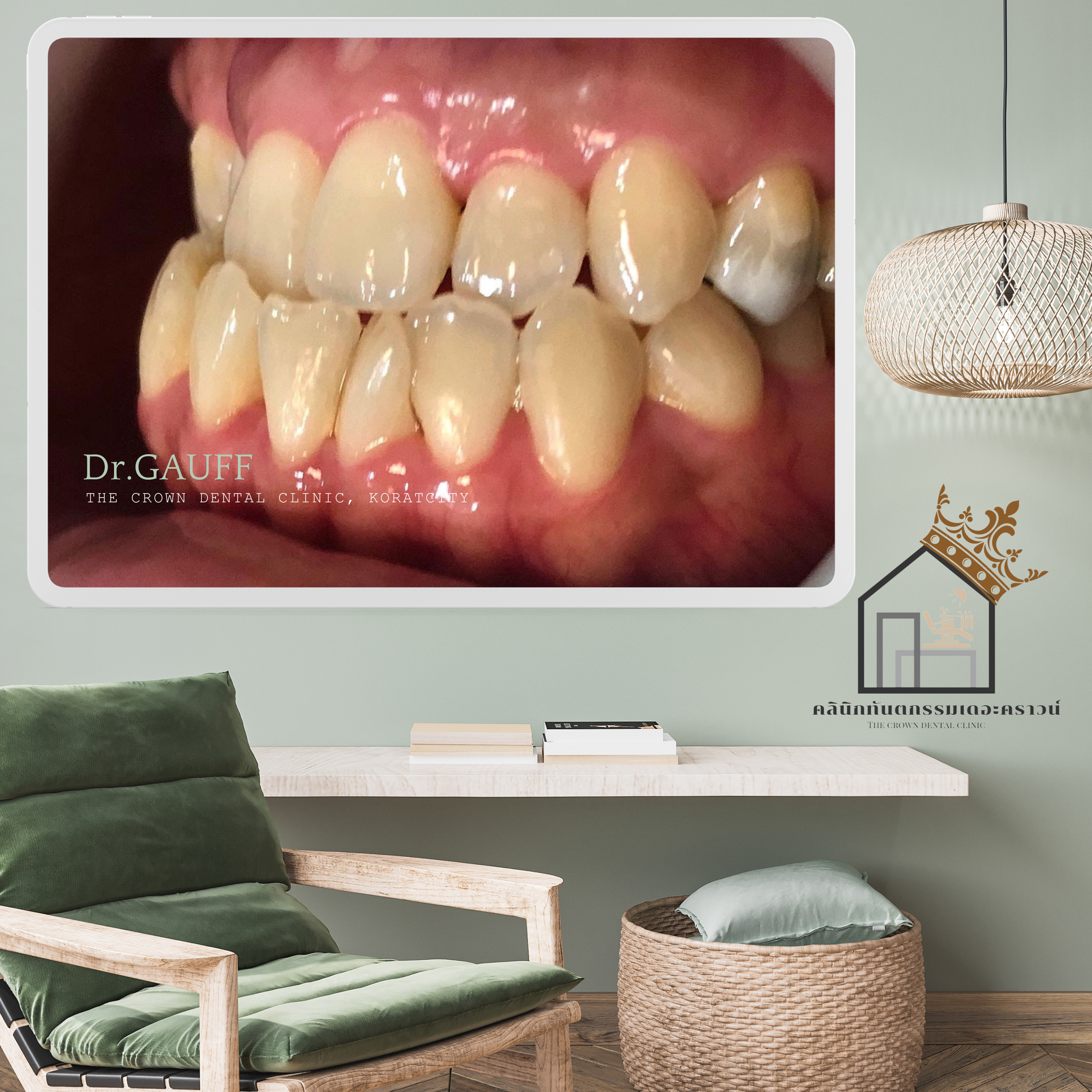
จะสังเกตได้ว่าซี่ฟันหน้า พบเหงือกร่น เป็นผลมาจากการผ่าฟันฝังซี่เขี้ยวบริเวณนี้ออกไป เป็นไปได้ค่อนข้างยากที่จะเคลื่อนฟันซี่นี้ลงมาให้เหลื่อมฟับฟันล่างได้เพิ่ม เนื่องจากร่างกายจะไม่ยอมให้สูญเสียกระดูกเพิ่ม ซึ่งมันจะทำให้เกิดโรคปริทันต์ที่รุนแรงมากขึ้น (เหงือกร่นมากขึ้น กระดูกละลายมากขึ้น ฟันก็จะโยกมากขึ้นตามมา) ดังนั้น ซี่นี้ก็จะคงสภาพไว้ที่ตำแหน่งนี้
ณ ปัจจุบัน คนไข้รายนี้ถอดเครื่องมือ และใส่เครื่องมือคงสภาพฟัน มาตรวจเช็คสุขภาพฟัน ขูดหินปูนทุกปี จากการติดตามอาการไม่มีอาการของข้อต่อขากรรไกรจากการสบฟัน ใช้งานได้ตามปกติ การยิ้ม การพูดรู้สึกสมมาตรมากขึ้น แนะนำเรื่องของการทำความสะอาดและติดตามอาการสม่ำเสมอ เพื่อเช็คฟันซี่หน้าที่เหงือกร่น
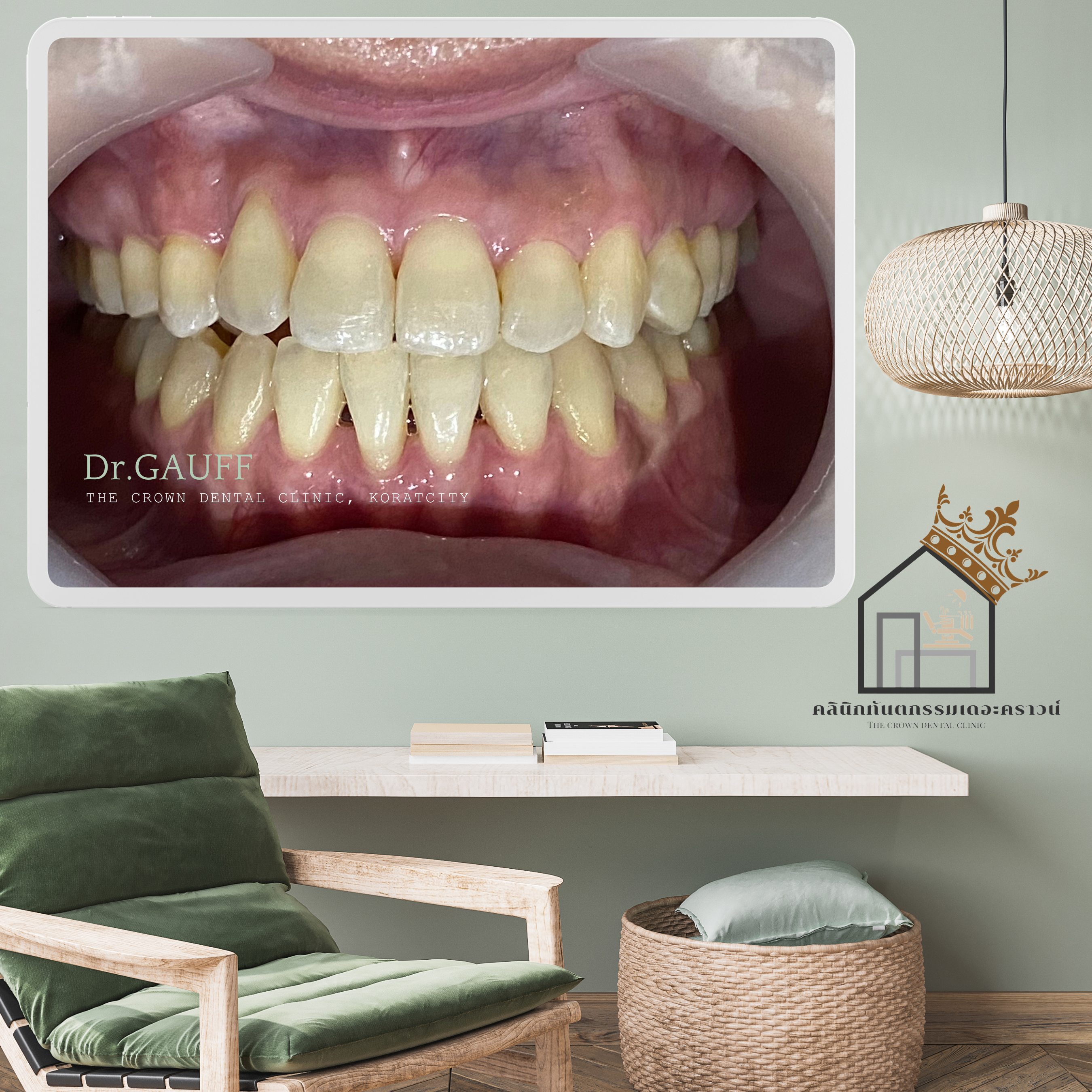
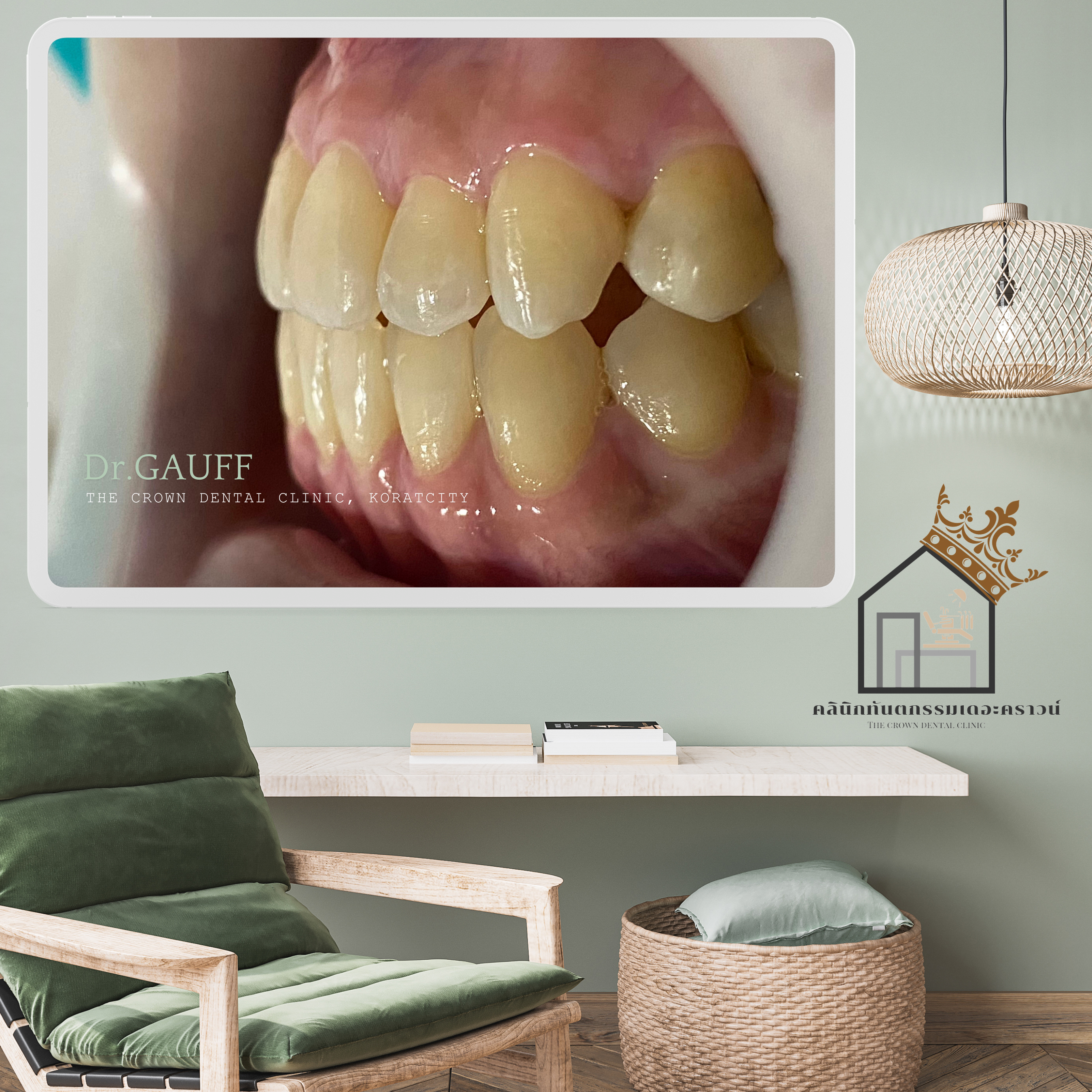
Orthodontic Case Review – The Crown Dental Clinic, KoratThis orthodontic case presented with a lower anterior crossbite (the lower front teeth overlapping the upper front teeth) and an inclined occlusal plane when viewed from the front. The patient also showed collapse of the right side of the jaw and dentition, resulting in facial asymmetry during smiling and speaking. Based on comprehensive clinical examination and radiographic evaluation, the case was deemed suitable for correction with orthodontic treatment.On the patient’s right side, the images reveal collapse in this region, and the upper right canine was clinically missing. Radiographic examination confirmed an impacted canine embedded in the bone. Surgical removal of the impacted tooth was considered to reduce the risk of serious pathologic lesions and because the impacted tooth could interfere with orthodontic tooth movement.However, an important consideration in removing this impacted canine was that the procedure would require removal of surrounding bone. Given the proximity of the impacted tooth to adjacent healthy teeth, there was a risk that postoperative periodontal complications could occur in the neighboring teeth, such as gingival recession, deep periodontal pockets, or tooth mobility.As observed, gingival recession was present on the anterior tooth in this area, likely as a consequence of the previous surgical removal of the impacted canine. It was considered quite difficult to further move this tooth downward to increase its overlap with the lower teeth, as the body tends to resist additional bone loss. Further movement could potentially exacerbate periodontal disease—leading to increased gingival recession, further bone resorption, and greater tooth mobility. Therefore, this tooth was maintained at its existing position.At present, the patient has completed orthodontic treatment, the appliances have been removed, and retainers are in use. The patient returns annually for dental check-ups and scaling. Follow-up evaluations show no temporomandibular joint symptoms related to occlusion, normal function, and improved facial symmetry during smiling and speaking. Ongoing oral hygiene instruction and regular monitoring have been emphasized, particularly to observe the anterior tooth with gingival recession.

ขอบคุณที่ติดตามอ่านบทความ คุณหมอกอล์ฟ คลินิกทันตกรรมเดอะคราวน์โคราช


